Types of Accounts
Meaning of Account :
In accounting, the transactions that occurred during a year we often use many accounts. It helps to organize the accounting transactions in a structured and useful manner. For example, the term cash account is used to record all the cash receipts and payments and any adjustments involving cash. And the term bank account is used in accounting to record all the transactions related to the bank.
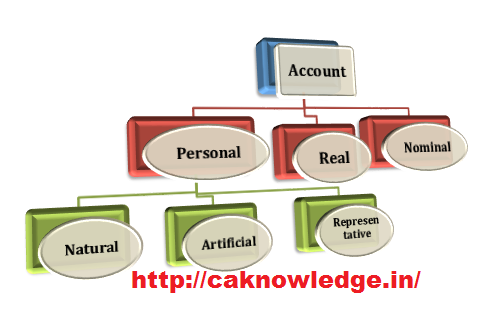
A) Personal account :
A personal account is used to denote individuals and firms, organizations. Simply it is an account to organize the transactions related to natural and artificial persons. Example: Mr manoj has taken a loan of 1000 from the company xyz. Here in the books of xyz Mr manoj is a personal account and in the books of Manoj , xyz is a personal account.
Personal account can be classified into 3 types as :
(1) Natural personal accounts : These are the accounts which denotes natural human beings like Ajay, Bali , Chandan , Diya etc. (2) Artificial personal accounts : These are the accounts which are used to indicate that transactions occur with entities which have a separate legal identity which they possess in the eyes of law.For example ABC Ltd., Government , State bank of India etc., (3) Representative personal account : These are the accounts which are indirectly related to the natural and artificial persons. For example Prepaid account, capital account, outstanding liability account, etc.,
B) Real account :
A real account is used to record the transactions related to assets. The term assets include both tangible and intangible. Tangible assets are the assets held by the business, which can be seen and touched. Where intangible assets are the assets which can’t be seen and touched. For example Plant and machinery, Buildings, cash account come under real account. And intangible assets like goodwill , patents , trademarks also come under real account.
C) Nominal account :
Accounts which are related to expenses and incomes, losses and gains.For example interest paid, administration charges, stipend paid etc.,
Accounting Standard 13What is Debit and credit explainedWhat Is Debit Note and Credit NoteAccounting Standard 15
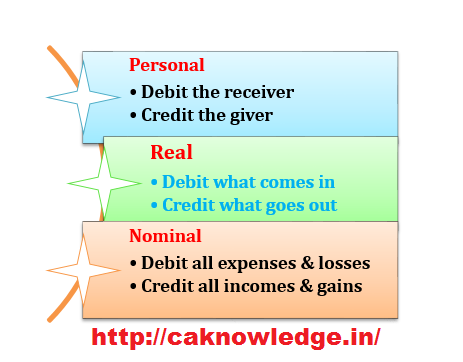
Golden rules of accounting :
(1) Personal account : a) Debit the receiverb) Credit the giver. (2) Real account : a) Debit what comes in.b) Credit what goes out. (3) Nominal account : a) Debit all expenses and losses.b) Credit all incomes and gains. Illustration : Mr venkat has brought 50 lakhs cash into his newly commenced business and hired 10 employees to run it. As his concern is engaged in trading of goods and rendering of some services related to it, he mainly incurs expenses for paying the employees, and purchasing the goods apart from the regular administration needs. Now(1) When he brought cash into the business As cash is a real account we have to Debit what comes into business and credit what goes out.And Capital account is a a representative personal account as it indirectly indicates venkat’s contributed funds to business , so Credit the giver rule comes into picture. And the entry is Cash A/c DrTo Capital A/c.
When ha pays salary :
Salary is an expenses to business so it is to be categorized in Nominal account and Debit all expenses and losses rule is applicable here. When we pay cash as salary , it goes out of business so Credit what goes out of real account rule comes into picture. And the entry is Salary A/c. DrTo Cash A/c.
When he purchases goods
Purchases is in the nature of expenses so Debit all expenses rule is to be applied.As we are paying the cash for purchasing goods it is to be credited as it goes out of business. Purchases A/c. DrTo Cash A/c. Thanks Recommended Articles
Golden Rules of AccountingAccounting StandardWhat Is Debit Note and Credit NoteFund Flow StatementAccounting Rate of Return