Taxable Event in GST Regime
The new tax reforming law which is going to be reality by July 2017 is proposing to shift all such different levies under various taxation under one single levy and under single law. The new taxable event which will subsume all the above mentioned present levied is named as ‘Supply’. In other words, under GST regime, if there is Supply then there is levy and liability to pay tax will arise. Under the previous regime taxable event for various taxes were different. For example, for excise duty the taxable event was manufacture or production of goods in India. Similarly, for services the taxable event was when a service was provided or agreed to be provided. Under CST and VAT it was sale of goods. Thus, all this led to lot of confusion in determining taxes to be paid. To replace such multiple taxable events, GST has brought a single and uniform taxable event, which is, supply and tax will accrue to the taxing authority which has jurisdiction over the place of consumption and will be the place of supply in most cases.
Meaning of Supply
As per Section 7 of the CGST law, the meaning of supply is defined as under:-
The term supply includes-
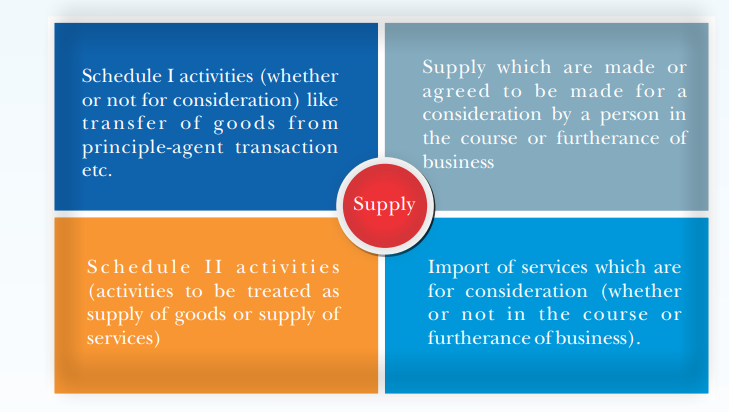
(a) all forms of supply of goods or services or both such as sale, transfer, barter, exchange, licence, rental, lease or disposal made or agreed to be made for a consideration by a person in the course or furtherance of business; Analysis – It largely includes all sorts of transactions which are presently covered under sales tax, excise and service tax. It seems that it takes land also in its purview and therefore there is specific exclusion of land from the term supply as mentioned in later part of this article. (b) import of services for a consideration whether or not in the course or furtherance of business; Analysis – This provision seeks to consider import of services for a consideration irrespective of such services being used in the course or furtherance of business. (c) the activities specified in Schedule I, made or agreed to be made without a consideration; and Analysis – This sub-section seeks to specify the various activities which shall be considered as supply even without consideration. The details of such activities are :-
Permanent transfer or disposal of business assets where input tax credit has been availed on such Supply of goods or services or both between related persons or between distinct persons as specified in section 25, when made in the course or furtherance of business:Provided that gifts not exceeding fifty thousand rupees in value in a financial year by an employer to an employee shall not be treated as supply of goods or services or both.Supply of goods between agent and principal when they undertake to supply such goods on behalf of each otherImport of services by a taxable person from a related person or from any of his other establishments outside India, in the course or furtherance of business.
(d) the activities to be treated as supply of goods or supply of services as referred to in Schedule II. Analysis – Earlier the activities specified in Schedule II were covered in sub-section (2) of the definition of supply thereby restricting its scope to classification of goods and services. But as with the change Introduced In first sub-section itself, the activities mentioned in this sub-section not only provides for classification between goods and services but also specifies levy of tax on the goods and services mentioned in this Schedule.
Exclusion from the definition of supply –
The following actives are excluded from the definition of supply-
Services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his employment.Services by any court (District Court, High Court and Supreme Court) or Tribunal established under any law for the time being in force.The functions performed by the Members of Parliament, Members of State Legislature, Members of Panchayats, Members of Municipalities and Members of other local authorities.The duties performed by any person who holds any post in pursuance of the provisions of the Constitution in that capacityThe duties performed by any person as a Chairperson or a Member or a Director in a body established by the Central Government or a State Government or local authority and who is not deemed as an employee before the commencement of this clause.Services of funeral, burial, crematorium or mortuary including transportation of the deceased.Sale of land and, subject to clause (b) of paragraph 5 of Schedule II, sale of building.Actionable claims, other than lottery, betting and gambling.Such activities or transactions undertaken by the Central Government, a State Government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authorities, as may be notified by the Government on the recommendations of the Council, shall be treated neither as a supply of goods nor a supply of
Declared Supply of goods or services
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, specify, by notification, the transactions that are to be treated as—
a supply of goods and not as a supply of services; ora supply of services and not as a supply of goods.
Composite Supply
Composite supply means a supply made by a taxable person to a recipient comprising two or more supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof, which are naturally bundled and supplied in conjunction with each other in the ordinary course of business, one of which is a principal supply. Here, principal supply means the supply of goods or services which constitutes the predominant element of a composite supply and to which any other supply forming part of that composite supply is ancillary and does not constitute, for the recipient an aim in itself, but a means for better enjoyment of the principal supply. Taxability will be attracted as per provisions applicable to the principal supply. Examples :- Laptops with carry case, Machinery with installation, Travel with food, Stay with breakfast, etc Note:- The works contract services and restaurant and outdoor catering services are specifically covered within the meaning of composite supply. Mixed supply means two or more individual supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof, made in conjunction with each other by a taxable person for a single price where such supply does not constitute a composite supply. Taxability on mixed supply will be applicable at the highest tax rate as applicable on the supply if taxed individually.Mixed Supply Examples:- Tooth brush with tooth paste, Soap free with detergent, Buiscuits free with chips, etc.
Taxability on a composite or a mixed supply
A composite supply comprising two or more supplies, one of which is a principal supply, shall be treated as a supply of such principal supply. A mixed supply comprising two or more supplies shall be treated as a supply of that particular supply which attracts the highest rate of tax.
Conclusion
Thus the taxable event is going to shift to Supply and as there is difference in the nature of goods and services, a bifurcation between the two is kept so as to identify the time and place of supply for goods and services. Further, the concepts of mixed supply and composite supply also finds their place in the law so as to avoid confusion in case of bundled supplies. Recommended Articles
GST ScopeGST ReturnGST FormsGST RateGST RegistrationWhat is GST?GST Invoice FormatGST Composition SchemeHSN CodeGST LoginGST RulesGST StatusTrack GST ARNTime of Supply
If you have any query regarding “Taxable Event in GST Regime” then please tell us via below comment box…